Ilmu Pengetahuan – Sepertinya kita sering terjebak pada persoalan dasar ketika menyusun konsep saat akan berbicara dalam diskusi maupun waktu merumuskan penelitian. Semua itu terjadi karena kurang cakap memahami ilmu sebagai pengetahuan atau pengetahuan sebagai ilmu khususnya dalam dunia kesehatan.
Beranjak pada persoalannya, di artikel ini kita akan membahas secara meluas tentang ilmu pengetahuan dari sudut pandang penelitian berdasarkan beberapa referensi dan improvisasi admin. Silahkan simak penjelasannya secara seksama agar tidak terjebak dalam fallacy (sesat piker).
Sebagai pendahuluan, dalam Kamus Umum Bahasa Indonesia (1999) Penelitian diartikan sebagai kegiatan pengumpulan, pengolahan, analisis dan penyajian data yang dilakukan secara sistematis dan obyektif untuk memecahkan suatu persoalan atau menguji suatu hipotesis untuk mengembangkan prinsip-prinsip umum.

Sementara itu, Hadi (1993) mendefinisikan penelitian sebagai usaha untuk menemukan, mengembangkan, dan menguji kebenaran suatu pengetahuan yang dilakukan dengan menggunakan prosedur dan metode-metode ilmiah.
Both of these meanings indicate that research is a process or series which essentially consists of planned activities ranging from data collection (discovery), data processing, data analysis and presentation of research data with the aim of solving problems or finding new knowledge.
In general, new research can be done when a problem arises or a problem is found, either in the form of discrepancies in statements from reality or as an effort to do something better.
When research is looking for answers to a discrepancy in a statement, the results of the research produce something new as a rebuttal or limitation or support for the statement. In this condition, research is a process in the development of science .
Understanding Science
Science is a collection of knowledge arranged systematically and coherently. The scientific method or also known as the research method is a procedure or systematic steps in gaining knowledge. These systematic steps include:
- Identifying and Formulating the problem
- Develop a Thought Framework
- Formulating Hypotheses
- Testing the hypothesis
- Draw a conclusion
In other words, the scientific method is a way of acquiring and organizing knowledge. The difference between Knowledge and Science lies in: ” Knowledge ” is the material of science, and can only answer about what, while Science answers about why a fact or event “ .
Also Read: Indonesia’s Health Profile
So, science is a collection of knowledge in a particular field that is systematically arranged, can be studied and taught, and has a certain use value.
Knowledge Requirements
The requirement for science is to have scientific objects and methods, or to have the following dimensions / aspects.
Ontological Aspects
The ontological aspect , which is related to what science studies or with respect to the object of study. The ontological aspect concerns what one wants to know, what is thinking or what is the problem.
Example: The ontological aspect in economics is human behavior that is faced with the problem of limited human resources with unlimited needs.
Epistomological Aspects
Epistemological aspects , relating to how science studies the object of study by using certain methods, namely scientific methods or scientific methods supported by scientific thinking tools.
The scientific method is basically a combination of inductive thinking patterns (from specific things, analyzed into general things) and deductive thinking patterns. (from general things to specific things).
Inductive and deductive thinking patterns are also called the “ Logico-hypotetic-verification or“ Deducto-hypotetico-verification ”process, which consists of the following steps:
- Formulate problems
- Develop a frame of mind
- Formulate a hypothesis
- Testing the hypothesis
- Draw a conclusion
Axiological Aspects
Axiological aspects , with regard to aspects of use or benefits of science. The use value of science can be seen positively and normatively. Positively, the use value of science is to describe, explain and predict various phenomena in accordance with the object of study being studied.
Meanwhile, normatively, the use value of science is to control various phenomena in the desired direction. Normatively, the axiological aspects of science are closely related to values, ethics and moral considerations. In research, the axilogical aspects are described in the suggestions or recommendations of the research results.
Process and Stages
Broadly speaking, science is formed through the following processes and stages.
- Science studies phenomena
- These phenomena are abstracted into concepts and variables
- Concepts and variables are studied for the relationship based on proportions which are in the form of hypotheses
- Hypotheses are tested empirically into facts
- Weaving facts in a meaningful framework forms a theory
These theories constitute science. Scientific activity begins with the formulation of problems and the preparation of a frame of mind which then produces a repertoire of scientific knowledge (including theory and results of empirical research).
From this framework, a hypothesis arises to be tested using data, analysis, testing techniques (statistics) and a statistical conclusion is drawn. If the hypothesis is accepted, it will become a treasure trove of scientific knowledge and if it is rejected, it will return to the preparation of a frame of mind to repeat the hypothesis until the conclusion is finally accepted.
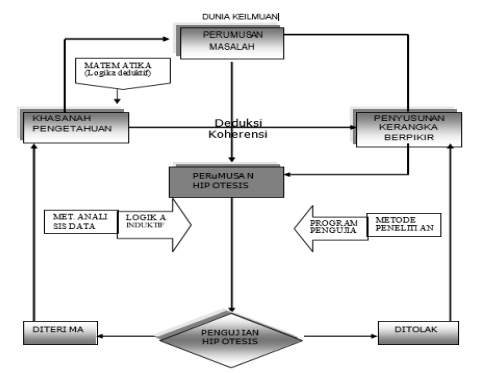
Scientific Activity Chart
For more details, pay attention to the Scientific Activity Chart as a Process and Scientific Method in the Scientific Activity as a Process chart below:
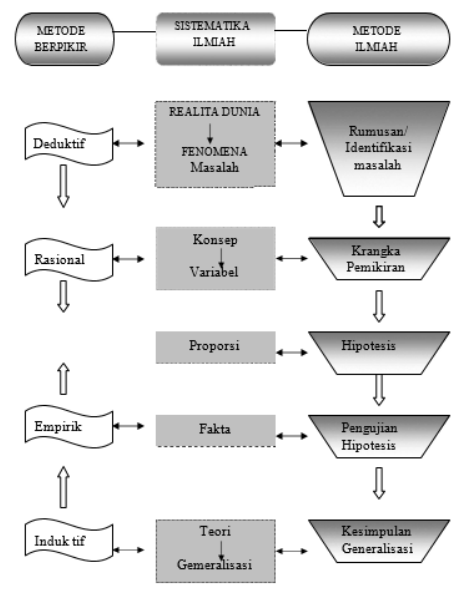
Hubungan Metode Berfikir, Sistematika Ilmiah dan Metode Ilmiah
Pada gambar berikut, Nampak bagaimana hubungan Metode Berfikir, Sistematika Ilmiah dan Metode Ilmiah:
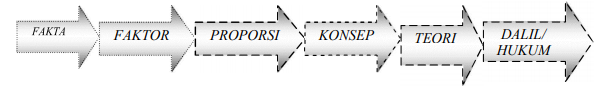
Komponen-Komponen Ilmu
Ilmu pengetahuan pada hakekatnya memiliki beberapa komponen sebagai berikut:
- Teori, yaitu generalisasi yang telah teruji kebenarannya secara ilmiah
- Fakta, keadaan sebenarnya (empirik) yang diwujudkan dalam jalinan dua konsep atau lebih.
- Fenomena, yaitu gejala dan kejadian yang ditangkap dengan panca indera (penglihatan, pendengaran, penciuman ,perasaan, perabaan), kemudian dijadikan konsep (istilah atau simbul) yang mengandung pengertian singkat dari fenomena
- Konsep, yaitu istilah atau simbul yang mengandung pengertian singkat dari fenomena.
Bila fakta yang satu mempengaruhi yang lain di sebut faktor. Hubungan antar faktor disebut proporsi. Proporsi inilah lazim disebut embrio teori. Bila sifat hubungan yang dimiliki proporsi telah diketahui, maka proporsi tersebut menjadi konsep lanjut (yang lebih tinggi dari konsep awal), yaitu menjadi teori hubungan. Bila teori itu sempat diuji berulang kali dan tetap bertahan, maka meningkat menjadi hukum atau dalil-dalil. Dalam Bagan Jalinan antara Komponen-komponen Ilmu tampak sebagai berikut.
Kelengkapan Ilmiah
Ilmu pengetahuan, memiliki juga kelengkapan-kelengkapan seperti:
Axio ma
Axio ma adalah pangkal dasar berfikir atau konsep dasar suatu ilmu, Misal : konsep dasar ilmu Anatomi fisiologi, tubuh merupakan suatu system, sehingga ada keterkaitan organ tubuh satu dengan yang lainnya, konsep dasar Tekniologi Lab Medik, analit yang ada pada cairan tubuh dapat dijadikan biomarker dari kondisi tubuh seseorang.
Data
Data adalah fakta-fakta sebagai bukti empirik. Ada tiga macam data, yaitu:
- Faktor endowment, yaitu faktor yang dianggap lestari (tidak b. bisa diubah oleh suatu disiplin ilmu tertentu).
- Variabel yaitu setiap gejala yang bisa diukur ( ada gejala yang tidak bisa diukur misalnya selera). Semua variabel terukur menurjut objektivitas, realiabilitas ilmiah dan validitasilmiah.
- Faktor Given, yaitu faktor yang dianggap relatif tetap(biasaanya dijadikan suatu asumsi dasar untuk keberlakuan hukum dalam ilmu pengetahuan).
Metode Berpikir
Metode Berfikir (Method of thinking) terdiri dari:
- Deduksi, yaitu membahas dari hal-hal yang umum dianalisis sampai dengan halhal yang khusus
- Induksi, yaitu data-data dianalisis untuk mebuat generalisasi
- Sistensis, yaitu paduan keduanya baik untuk verivikasi teori maupun untuk verifikasi dan generalisasi.
Kelengkapan ilmiah lainnya, meliputi:
- Model-model, misal model fungsi, model persamaan, model tabel, model grafik, model diagram, dll.
- Alat berfikir, misal grafis, diagramatis, statistis dan matematis
- Postulat ilmu terdiri dari hukum dasar yang jelas baik bersifat kausalitas maupun fungsionalitas
- Teknik penalaran (Method or reasioning), misal dalam ilmu ekonomi dapat disajikan dalam bentuk verbal, diagramatis, matematis, statistis dan grafis.
Objek Ilmu
Objek ilmu, setiap ilmu memiliki objek yaitu suatu objek yang dipelajari ilmu. Misal cara menganalisa fungsi ginjal, Cara mengevaluasi perkembangan suatu penyakit, cara melakukan validasi hasil pemeriksaan laboratorium.
Fungsi Ilmu
Fungsi ilmu, adalah menjelaskan, memprediksikan, mendeskripsikan, dan mengendalikan. Misal, fungsi ilmu ekonomi. a. Menjelaskan , memprediksi dan mendeskripsikan tentang cara kondisi kesehatan pasien; b. Menjelaskan dan mendeskripsikan cara mendiagnosa suatu penyakit.
Problem
Problem, semua ilmu pengetahuan diawali dengan adanya problem. Misal, problem dalam ilmu TLM adalah Hasil laboratorium harus berkualitas sedangkan pemahaman tentang Pengendalian Mutu Laboratorium belum merata pada semua tenaga TLM.
Ringkasan
Adapun poin penting sebagai ringkasan yang bisa kita petik dari artikel ini yakni:
- Ilmu pengetahuan berkembang dengan cara yang sistematis, penting untuk mengikuti tahapan pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan dalam menyelesaikan masalah secara ilmiah.
- Komponen-komponen ilmu pengetahuan penting dipahami untuk kemudahan dalam pengambangan ilmu pengetahuan.
This is a complete explanation of the science in the world of health. Please share this article if it is useful for your educational needs.